Radiation Therapy and Breast Cancer
 Radiation therapy is a critical treatment for breast cancer patients, playing a pivotal role in the management and care of individuals diagnosed with this disease.
Radiation therapy is a critical treatment for breast cancer patients, playing a pivotal role in the management and care of individuals diagnosed with this disease.
It uses high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancerous cells, and it is often a key part of the treatment plan after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence.
For nursing professionals, understanding the various aspects of radiation therapy nursing considerations and providing nursing care for breast cancer patients is essential.
This includes knowing the specific nursing interventions for radiation therapy, managing side effects of radiation therapy, providing patient education on radiation therapy, and ensuring proper post-radiation care for breast cancer patients.
In this essay, we will explore the principles, techniques, benefits, challenges, and future prospects of radiation therapy, with a focus on its role in breast cancer radiation therapy management and nursing care.

Struggling to meet your deadline?
Get your assignment on Radiation Therapy and Breast Cancer done by certified MDs and PhDs in the USA. ORDER NOW!
Nursing Role in Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
Nurses play a crucial role in the management of radiation therapy for breast cancer patients. They are involved in all phases of care, from assessing patients before treatment to providing support during and after radiation therapy. Breast cancer nursing guidelines are essential for nursing professionals in ensuring the correct delivery of radiation therapy. Nursing professionals help create radiation therapy treatment plans for breast cancer, tailored to individual patient needs, and assist with radiation oncology nursing assessments.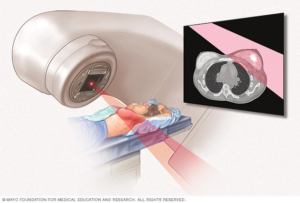
Nursing interventions for radiation therapy include monitoring for side effects of radiation therapy, managing pain, and ensuring that patients understand their treatment plan. Additionally, nurses are responsible for patient education on radiation therapy for breast cancer, explaining the benefits and risks of treatment, as well as the potential side effects. Nurses also ensure that patients adhere to radiation therapy treatment plans for breast cancer, track their progress, and offer emotional support throughout the process.
Radiation Therapy Techniques for Breast Cancer: Nursing Considerations
Radiation therapy techniques are tailored to the type and stage of cancer being treated. External beam radiation therapy is the most common method used for breast cancer radiation therapy. The radiation is directed at the tumor from outside the body using a linear accelerator. For some patients, more specialized techniques such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) or stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) may be used to provide highly targeted treatment with minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissues. External beam radiation therapy for breast cancer is most commonly used, and radiation oncology nurses need to be skilled in monitoring and managing potential side effects of radiation therapy during this process.
Other approaches, such as targeted radiation therapy for breast cancer, require careful consideration of nursing care practices. For example, radiation oncology nurses need to monitor patients for skin irritation, fatigue, and other common side effects of radiation therapy. They also need to assess for signs of more severe complications, such as radiation-induced burns or changes in breast tissue.
Common Side Effects of Radiation Therapy and Nursing Interventions
Side effects of radiation therapy are a common concern for nurses caring for breast cancer radiation therapy patients. These side effects can range from short-term symptoms like fatigue, skin irritation, and temporary breast swelling to long-term effects such as radiation-induced fibrosis or secondary cancers. Managing radiation therapy side effects is crucial to improving the patient’s overall experience and long-term recovery.
Nurses play a vital role in managing these side effects. Nursing interventions for radiation therapy may include advising patients on how to care for their skin, helping them manage fatigue through rest and nutrition, and providing emotional support to address any psychological stress caused by the treatment. Post-treatment care for breast cancer radiation therapy patients is essential for managing these ongoing issues. Patient education on radiation therapy for breast cancer is key to helping patients cope with these side effects and understand the importance of following the care guidelines provided by their healthcare team.
Personalized Radiation Treatment Plans for Breast Cancer Patients
In the field of radiation oncology, there is a growing emphasis on personalized treatment plans. Advances in radiation therapy techniques allow for treatment to be customized to the individual patient, taking into account factors such as tumor size, location, and the patient’s overall health. Personalized radiation treatment plans for breast cancer patients are developed by the healthcare team, including oncologists, radiologists, and nurses.
For radiation oncology nurses, understanding these individualized plans is essential for ensuring that patients receive the best possible care. Radiation oncology nursing assessments are critical for monitoring how well the treatment is working and how the patient is tolerating it. Nurses should be able to recognize signs of treatment-related complications early, making them an integral part of the patient care team in breast cancer radiation therapy.
Managing the Emotional and Physical Effects of Radiation Therapy in Nursing
Managing the emotional and physical effects of radiation therapy is an essential part of nursing care for breast cancer patients. Radiation therapy can have significant psychological and physical impacts, including feelings of anxiety, depression, and body image concerns. Best practices for nursing care in breast cancer radiation therapy should include comprehensive support, ensuring both emotional and physical recovery.
Nursing interventions should address both the emotional and physical aspects of treatment. Nurses must provide psychological support and be sensitive to the emotional challenges that patients face as they undergo radiation therapy. This includes actively listening to patients, offering counseling resources, and connecting them with support groups. Managing radiation therapy side effects effectively also includes helping patients manage physical discomfort, providing resources for physical therapy, and offering advice for coping with radiation therapy recovery for breast cancer patients.
Patient Education on Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
An essential component of nursing care for breast cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy is patient education on radiation therapy. Nurses must educate patients about the radiation therapy process, what to expect during treatment, potential side effects, and how to care for themselves during and after treatment. Teaching patients about side effects of radiation therapy, such as fatigue and skin irritation, and ways to manage them effectively, can significantly improve their overall treatment experience.
Post-radiation care for breast cancer patients is another important area for nursing education. Nurses should provide clear instructions on how to cope with any post-treatment side effects and emphasize the importance of attending follow-up appointments to monitor for delayed effects of radiation. By providing custom nursing papers, nurses can ensure that patients have access to comprehensive resources that will help them navigate their treatment and recovery.
Post-Treatment Nursing Care for Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiation Therapy
Post-treatment care for breast cancer radiation therapy patients is crucial to ensuring optimal recovery. After radiation therapy, nurses monitor for any lingering or delayed side effects, such as changes in skin texture, pain, or swelling. Post-radiation care involves assessing the patient’s physical and emotional recovery, providing support for managing any lingering effects of radiation therapy, and facilitating a smooth transition to the next phase of cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy or ongoing surveillance.
Role of Oncology Nurses in the Radiation Therapy Process
The role of radiation oncology nurses in breast cancer care is multifaceted. Nurses serve as the primary point of contact for patients, providing care, support, and education throughout the treatment journey. Radiation oncology nurses are involved in the planning phase, working alongside radiation oncologists to ensure that the treatment plan is tailored to the individual patient’s needs. They monitor patients during treatment, assess for side effects, and provide interventions when necessary. Oncology nurses also support the patient’s emotional well-being, helping them navigate the stress and uncertainty that often accompany cancer treatment.
Best Practices for Monitoring and Supporting Breast Cancer Patients During Radiation Therapy
Best practices for nursing care in breast cancer radiation therapy include regular monitoring for both physical and emotional changes. Nurses should use cancer treatment nursing care plans to guide their interventions, tracking symptoms, offering resources for pain management, and ensuring that the patient has access to necessary supportive services. Nurses are also crucial in educating patients on how to handle any side effects they may experience and ensuring that they feel supported and informed throughout their treatment.
Conclusion
Radiation therapy is a cornerstone of breast cancer treatment and offers significant benefits in terms of tumor eradication, recurrence prevention, and survival rates. However, it comes with challenges, particularly in managing the side effects and ensuring comprehensive nursing care. Through effective nursing interventions, patient education, and support, oncology nurses play a critical role in improving outcomes for breast cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy. By understanding radiation oncology nursing considerations and following best practices for nursing care in breast cancer radiation therapy, nurses can help patients navigate their treatment journey with confidence and hope for the future.

Dont wait until the last minute.
Provide your requirements and let our native nursing writers deliver your assignments ASAP.

