Nurse 514 Topic 1: Healthcare System Evolution and Nursing Roles
 The landscape of the U.S. healthcare system has undergone a remarkable transformation.
The landscape of the U.S. healthcare system has undergone a remarkable transformation.
Initially, it was primarily focused on addressing infectious and acute diseases, with a limited understanding of the causes of diseases.
During this period, healthcare providers often attributed diseases to supernatural phenomena and focused on reducing mortality rates.
In this context, the primary goal was to enhance the management of these conditions and prevent deaths.
However, as time passed, the healthcare system evolved in response to increased scientific research and evidence. This research shed light on the growing prevalence of chronic conditions, which could be attributed to a lack of emphasis on health promotion and the rise of sedentary lifestyles (Fisk et al., 2020). The shift in focus toward chronic disease management nursing and chronic disease prevention became essential, with health promotion strategies and preventive healthcare gaining more attention as ways to improve long-term health outcomes.

Struggling to meet your deadline?
Get your assignment on Nurse 514 Topic 1: Healthcare System Evolution and Nursing Roles done by certified MDs and PhDs in the USA. ORDER NOW!
The turning point in the transformation of the healthcare system began with the greater adoption of technology and scientific research highlighting the benefits of health promotion, preventive care, and evidence-based medicine. This shift laid the foundation for the value-based healthcare model, where quality takes precedence over quantity. This model not only focuses on improving patient outcomes but also integrates various nursing quality metrics to assess the effectiveness of care.
The value-based model leverages healthcare technology in nursing to enhance the delivery of care and places a strong emphasis on bridging gaps in healthcare through the use of innovative technologies. For example, telemedicine nursing and remote patient monitoring have allowed nurses to deliver nurse-led care and support patients in the comfort of their homes. Moreover, nursing informatics and the use of electronic health records in nursing streamline communication between primary care providers and patients, improving nurse-patient communication and promoting patient-centered care models.
This shift has had a profound impact on the roles and responsibilities of advanced registered nurses (ARNs) in several ways. Firstly, ARNs have taken on the role of primary care providers and patient advocates, ensuring that all segments of the population have access to healthcare (Pittman et al., 2019). As nurse practitioners (NPs), ARNs are now providing essential care for chronic conditions, leading efforts in chronic disease care coordination, and empowering patients to manage their health more effectively.
Secondly, advanced registered nurses work in collaboration with other healthcare professionals within multidisciplinary care teams, delivering care to patients across diverse settings. Multidisciplinary care teams bring together a range of healthcare professionals, all of whom work toward the same goal: improving patient outcomes through nursing. ARNs, as nurse practitioners, are key members of these teams, working alongside physicians, social workers, and other healthcare providers to improve the coordination of care.
In their capacity as primary care providers, these nurses have expanded their roles and responsibilities to serve a wider range of populations while maintaining a commitment to delivering high-quality care that leads to improved outcomes. They are also at the forefront of implementing innovative technologies and transformative approaches to enhance the quality of nursing care outcomes.
The evolving trends, such as the increased integration of technology, the expansion of nurse-led care, and the emphasis on improving access and quality, will undoubtedly impact the nursing profession. Nurses will be expected to assume a broader spectrum of roles and responsibilities. This evolution suggests that nurses will continue to specialize to meet the diverse needs of their patients (Rambur et al., 2019). As the demand for quality chronic disease management nursing increases, there will be a stronger need for specialized roles such as population health nursing and the integration of nursing education and nursing professional development.
Advanced registered nurses will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare by becoming equal partners and providers alongside physicians. They will contribute to enhancing access to care and bridging the healthcare workforce shortage gap. By advocating for policies that support the nursing role in healthcare and nursing role in health policy, ARNs will be able to address nurse staffing issues and nurse burnout solutions. Moreover, they will develop and implement more effective interventions to enhance population health across different care settings and age groups. This transformation marks an exciting and dynamic era for nursing professionals.
 Additionally, nursing leadership will play a critical role in guiding the evolution of the healthcare system. Nurses in health policy and nursing leadership positions are essential for creating a more equitable healthcare system. They will also continue to focus on healthcare equity, ensuring that underserved populations have access to necessary care. The ongoing commitment to nursing certifications, continuing education for nurses, and specialization in nursing will ensure that the workforce remains adaptable and ready to meet future healthcare challenges.
Additionally, nursing leadership will play a critical role in guiding the evolution of the healthcare system. Nurses in health policy and nursing leadership positions are essential for creating a more equitable healthcare system. They will also continue to focus on healthcare equity, ensuring that underserved populations have access to necessary care. The ongoing commitment to nursing certifications, continuing education for nurses, and specialization in nursing will ensure that the workforce remains adaptable and ready to meet future healthcare challenges.
This transformation in the healthcare system underscores the nursing role in healthcare, highlighting the significance of nursing advocacy, nurse-patient communication, and the critical need for a strong, diverse nursing workforce. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the future of nursing will be shaped by nurses’ ability to adapt, specialize, and take on leadership roles to improve healthcare access and healthcare delivery across the nation.
NUR-514 Topic 1 DQ 1: Health Care Systems, Organizational Relationships, and Interprofessional Health Care Environments References
Fisk, M., Livingstone, A., & Pit, S. W. (2020). Telehealth in the context of COVID-19: Changing perspectives in Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Journal of Medical Internet research, 22(6), e19264. DOI: 10.2196/19264.
Pittman, P., Rambur, B., Birch, S., Chan, G. K., Cooke, C., Cummins, M., … & Trautman, D.
(2021). Value-based payment: What does it mean for nurses? Nursing Administration Quarterly, 45(3), 179-186. DOI: 10.2196/19264.
Rambur, B., Palumbo, M. V., & Nurkanovic, M. (2019). Prevalence of telehealth in nursing:
Implications for regulation and education in the era of value-based care. Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice, 20(2), 64-73. DOI: 10.1177/1527154419836752.
Discussion Question 1: Value-Based Healthcare and Nursing Roles
The landscape of healthcare delivery continually evolves in response to shifting patient needs and changing care models. In tandem with these shifts, the U.S. healthcare system has undergone substantial transformations to ensure that individuals and communities can lead healthy and productive lives. Health policies and support programs have also adapted as circumstances demand. Among the notable evolutions is the transition to value-based healthcare, which carries profound implications for the nursing role in healthcare.
In essence, the shift to value-based healthcare signifies a departure from the traditional volume-based care approach towards a model centered on the quality of care. In this model, healthcare providers, including advanced registered nurses (ARNs), receive incentives based on the quality of care they deliver rather than the sheer quantity. The overarching objective is to overhaul healthcare delivery to generate more value for patients, with an emphasis on patient-centered care models (Teisberg et al., 2020).
With this goal in mind, healthcare providers increasingly concentrate on optimizing patient outcomes through evidence-based practice, reducing costs, and fostering healthy lifestyles. Consequently, the roles and responsibilities of advanced practice nursing, especially for nurse practitioners (NPs), undergo a transformation, with a heightened focus on care quality and patient satisfaction. Nurses now play a key role in improving healthcare outcomes, ensuring that patients receive high-quality care that is also cost-effective.
Instead of predominantly functioning as care providers, the shift to value-based care encourages nurses to take on the roles of innovators and change agents (Colldén & Hellström, 2018). This implies that advanced registered nurses must fully embrace their transformative role, ensuring that the quality of care aligns with patient needs and that patients receive services that are not only prompt but also highly satisfactory. This shift also requires nurses to work closely within multidisciplinary care teams, ensuring that care delivery is holistic and patient-centered, driving better outcomes for those under their care.
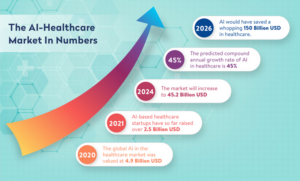
Several significant evolving trends are currently shaping the healthcare landscape. These include the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI), the rise of remote and virtual care, and the shift towards data-driven practices. These trends will have a profound impact on the healthcare system by driving the greater adoption of healthcare technology in nursing and nursing informatics. Technologies such as electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine nursing, and remote patient monitoring are becoming essential tools in nursing practice. However, as Wirth et al. (2021) have suggested, a technology-driven practice also brings heightened concerns regarding privacy and security, underscoring the need for nursing leadership in overseeing these innovations while ensuring that patient confidentiality is maintained.
This integration of technology will necessitate the presence of healthcare providers with specialized skills, such as nurse informaticists, who can bridge the gap between technology and patient care. These nurses will be instrumental in ensuring that electronic health records and telemedicine nursing systems are designed and implemented effectively, aligning with best practices and patient needs. They will also advocate for nursing role in healthcare policies that promote the use of technology to improve care while maintaining patient safety and satisfaction.
 As these trends unfold, advanced registered nurses will exert considerable influence on the direction of healthcare. They will play pivotal roles in guiding organizations in system design and implementation, ensuring that these systems harness the potential of technology-driven practices effectively. Additionally, nurse practitioners and ARNs will assume essential roles in patient education, health promotion strategies, policymaking, and the development of care models that optimize quality, safety, and, most importantly, overall patient satisfaction. The increased role of nurses in health policy will be crucial in ensuring that healthcare systems remain responsive to both technological advancements and the evolving needs of patients.
As these trends unfold, advanced registered nurses will exert considerable influence on the direction of healthcare. They will play pivotal roles in guiding organizations in system design and implementation, ensuring that these systems harness the potential of technology-driven practices effectively. Additionally, nurse practitioners and ARNs will assume essential roles in patient education, health promotion strategies, policymaking, and the development of care models that optimize quality, safety, and, most importantly, overall patient satisfaction. The increased role of nurses in health policy will be crucial in ensuring that healthcare systems remain responsive to both technological advancements and the evolving needs of patients.
This transformation heralds a dynamic era for nursing professionals as they continue to adapt and lead in a healthcare environment marked by change and innovation. Nursing leadership will be key to ensuring that the future of healthcare is patient-centered, with nurse-led care and multidisciplinary care teams working together to meet the demands of a rapidly changing healthcare landscape. Nurses in health policy will also be instrumental in advocating for healthcare equity, ensuring that underserved populations have access to the high-quality, patient-centered care they need to live healthy and productive lives.
Ultimately, the shift to value-based care underscores the critical role of advanced registered nurses in shaping the future of healthcare. Through their leadership, advocacy, and commitment to improving patient outcomes through nursing, nurses will continue to drive the healthcare system toward a more effective, efficient, and compassionate model of care.
NUR-514 Topic 1 DQ 1: Health Care Systems, Organizational Relationships, and Interprofessional Health Care Environments References
Colldén, C., & Hellström, A. (2018). Value-based healthcare translated: A complementary view of implementation. BMC Health Services Research, 18(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-018-3488-9
Teisberg, E., Wallace, S., & O’Hara, S. (2020). Defining and implementing value-based health care: A strategic framework. Academic medicine: Journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges, 95(5), 682–685. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000003122
Wirth, F. N., Meurers, T., Johns, M., & Prasser, F. (2021). Privacy-preserving data sharing infrastructures for medical research: Systematization and comparison. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 21(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-021-01602-x

Dont wait until the last minute.
Provide your requirements and let our native nursing writers deliver your assignments ASAP.

