Obstetrics/Gynecology Nursing
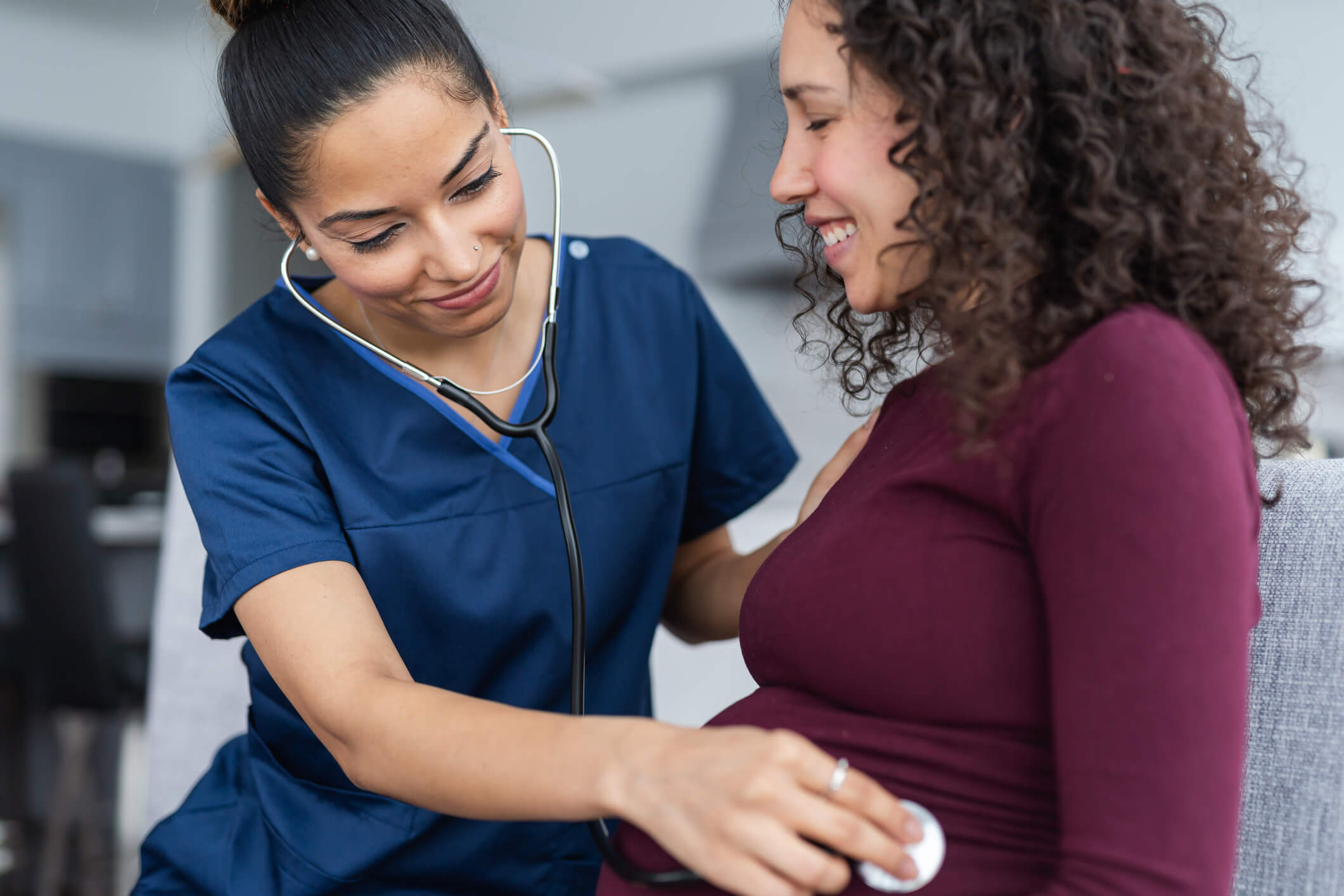 Overview: Obstetrics nursing is a specialized field of nursing that focuses on providing care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the immediate postpartum period.
Overview: Obstetrics nursing is a specialized field of nursing that focuses on providing care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the immediate postpartum period.
It also involves caring for newborns, and women experiencing pregnancy-related complications. Nurses in this field are essential in ensuring the health and safety of both mothers and their babies, offering support and guidance throughout the pregnancy journey.
The role of an obstetrics nurse, or OB/GYN nurse, is multifaceted and includes responsibilities in labor and delivery, prenatal care, and postpartum nursing care. This career offers opportunities for advancement and a chance to specialize in areas like high-risk obstetrics nursing, neonatal care, or even becoming a nurse practitioner in obstetrics.
What Is Obstetrics Nursing?
Obstetrics nursing is a subfield within women’s health nursing, focusing on the care of women and infants during pregnancy, labor, delivery, and the early postpartum period. Obstetrics nurses work in a variety of healthcare settings, including labor and delivery units, women’s health clinics, and postpartum care units. They collaborate with obstetricians, nurse midwives, and OB/GYN nurse practitioners (NPs) to deliver care, and often have a strong role in educating and supporting expectant mothers and families.

Struggling to meet your deadline?
Get your assignment on Obstetrics/Gynecology Nursing done by certified MDs and PhDs in the USA. ORDER NOW!
Becoming an Obstetrics Nurse
Duration: It typically takes 2 to 4 years to become an obstetrics nurse.
Job Outlook: The job outlook for registered nurses (RNs) is projected to grow by 7% between 2019 and 2029.
Average Earnings: RNs, on average, have an earning potential of $75,330 per year.
Key Roles of an Obstetrics Nurse
The role of an obstetrics nurse includes a wide range of responsibilities:
- Pregnancy Care: Monitoring the health of pregnant women and their fetuses, performing assessments, and providing education on prenatal care.
- Labor and Delivery Support: Assisting with the delivery process, monitoring labor progress, and providing emotional and physical support during childbirth.
- Postpartum Care: Caring for mothers after birth, supporting breastfeeding, and addressing any complications that may arise post-delivery.
- Neonatal Care: Assisting with newborn care, especially if there are complications that require special attention.
Becoming an Obstetrics Nurse
Education Requirements for Obstetrics Nurses
To become an obstetrics nurse, you typically need to earn an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) or Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN). BSN programs are preferred for those aiming for advanced positions or specialization. For nurse practitioners in obstetrics (OB/GYN NPs), a BSN and a master’s degree in nursing (MSN) are required.
Obstetrics Nursing Certification
Certifications, such as the Inpatient Obstetric Nursing Certification (RNC-OB) from the National Certification Corporation, can help validate expertise in obstetrics nursing. Obstetrics nurses often pursue this certification after gaining two years of experience and 2,000 hours in obstetrics care. Additionally, OB/GYN nurse practitioner certification is available for advanced practice nurses.
Steps to Becoming an OB/GYN Nurse
- Earn your RN: Complete an ADN or BSN program and pass the NCLEX-RN to obtain your registered nurse (RN) licensure.
- Gain Experience: Work in obstetrics to develop your skills in pregnancy care, labor and delivery, and postpartum care.
- Pursue Certification: Consider obtaining specialized certifications in obstetrics nursing, such as RNC-OB, to enhance your qualifications.
- Advanced Education (Optional): For career advancement, you may choose to become an OB/GYN nurse practitioner or a certified nurse-midwife (CNM), both of which require additional education and certification.
Key Responsibilities of an Obstetrics Nurse
Obstetrics nurses are responsible for various tasks that support the health of the mother and baby during pregnancy and childbirth:
Responsibilities During Pregnancy and Prenatal Care
- Educating mothers on healthy pregnancy practices, including nutrition and exercise.
- Monitoring fetal development and maternal health through routine tests and assessments.
- Assisting with prenatal screenings and educating patients about birth plans.
Responsibilities During Labor and Delivery
- Monitoring the progress of labor and ensuring the safety of the mother and baby.
- Assisting during childbirth by helping manage pain, providing emotional support, and communicating with the healthcare team.
- Assisting with cesarean sections (C-sections) if necessary.

Postpartum Care and Newborn Care
- Monitoring the physical and emotional well-being of the mother after childbirth.
- Supporting new mothers with breastfeeding, newborn care, and addressing any complications.
- Educating mothers on infant care, such as diapering, feeding, and general health.
Obstetrics Nurse Career Outlook
Job Market for Obstetrics Nurses
The demand for obstetrics nurses is strong, with the healthcare industry continuing to grow, especially as more women are seeking prenatal and maternal care. Registered nurses, in general, have a job growth projection of 7% between 2019 and 2029, which is faster than the average for all occupations. However, the job outlook for obstetrics nurses may vary depending on geographic location and local birth rates.
Job Outlook and Growth for Obstetrics Nurses (2024 and Beyond)
The demand for obstetrics nurses is expected to remain steady, driven by an aging population and increasing focus on maternal and fetal health. As healthcare expands and more focus is placed on maternal health outcomes, obstetrics nursing careers are likely to experience growth.
Salary Expectations for OB/GYN Nurses
The average salary for an OB/GYN nurse is around $61,520 per year, with salaries ranging from $45,000 to $104,000 depending on experience and location. Labor and delivery nurse salaries also vary but typically range from $60,000 to $80,000 annually. Obstetrics nurse practitioners typically earn a higher salary, with a median annual wage of $111,680, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Advancement Opportunities in Obstetrics Nursing
Obstetrics nurses can pursue various career advancement paths, including:
How to Advance Your Career in Obstetrics Nursing
- Obstetrics Nurse Practitioner (NP): Becoming an OB/GYN NP allows you to take on more advanced clinical roles, such as performing exams, diagnosing, and prescribing medications.
- Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM): Becoming a nurse midwife offers another route for specialization in maternal and reproductive health.
- Management Roles: Obstetrics nurses can move into management or leadership roles within labor and delivery units, clinics, or hospitals.
OB/GYN Nurse Practitioner and Nurse Midwife Roles
As an OB/GYN nurse practitioner or certified nurse midwife, you can take on more independent responsibilities in women’s health. These roles allow for more autonomy and the opportunity to oversee the birthing process, prescribe medications, and provide specialized care for women during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum.
Work Environments for Obstetrics Nurses
Obstetrics nurses work in several settings, including:
Obstetrics Nurses in Labor and Delivery Units
Labor and delivery units are one of the primary workplaces for obstetrics nurses. Here, they assist with deliveries, provide emergency care, and ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
Obstetrics Nurses in Prenatal Clinics and Women’s Health Clinics
In these settings, obstetrics nurses focus on prenatal education, routine testing, and monitoring maternal and fetal health.
Obstetrics Nurses in Postpartum Care Units
These nurses provide care for mothers and newborns in the immediate postpartum period, ensuring proper recovery and assisting with breastfeeding and infant care.
Obstetrics Nursing Specializations
High-Risk Obstetrics Nursing
Some obstetrics nurses specialize in high-risk pregnancies, providing care for women who have medical complications or multiple pregnancies. These nurses often work closely with other healthcare providers in specialized maternal and fetal care units.
Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing vs Obstetrics Nursing
While neonatal nurses focus on the care of newborns, particularly those with health complications, obstetrics nurses focus on the mother and the process of childbirth. The two roles overlap, but obstetrics nurses are primarily concerned with pregnancy and childbirth, while neonatal nurses care for the baby after birth.
Perinatal and Prenatal Education Roles
Obstetrics nurses play an essential role in prenatal education, providing expectant mothers with information about childbirth, nutrition, and infant care, helping them prepare for a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Differences Between Neonatal Nurses and Obstetrics Nurses
Neonatal Nurse Responsibilities
Neonatal nurses care for newborns, especially those with health complications, in settings like neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). They are more focused on post-birth care and managing infant health problems.
Obstetrics Nurse Responsibilities
Obstetrics nurses primarily care for women during pregnancy, labor, and delivery, supporting both the mother and fetus. Their responsibilities also include monitoring the health of the mother and fetus during pregnancy and providing support during childbirth.
Challenges and Rewards of Obstetrics Nursing
Emotional Challenges in Obstetrics Nursing
Working with pregnant women, newborns, and their families can be emotionally intense. Obstetrics nurses must often manage stressful situations, such as complications during labor or delivery, and provide emotional support to families.
Rewarding Aspects of Obstetrics Nursing
The rewards of obstetrics nursing include the joy of helping bring new life into the world and the opportunity to support families during one of the most significant events in their lives. Nurses also find fulfillment in providing care to mothers, ensuring their safety, and educating them on the best practices for health and infant care.
FAQs About Obstetrics Nursing
What Does an Obstetrics Nurse Do?
An obstetrics nurse cares for women throughout pregnancy, labor, and the postpartum period, as well as for newborns. Their role includes monitoring health, assisting with deliveries, and educating mothers about pregnancy, childbirth, and infant care.
How Long Does It Take to Become an Obstetrics Nurse?
It typically takes 2-4 years to become an obstetrics nurse, depending on whether you pursue an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) or a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN). Further specialization, such as becoming an OB/GYN nurse practitioner, requires additional education.
What Are the Salaries for OB/GYN Nurses?
The average salary for an OB/GYN nurse is about $61,520 per year, though this can vary based on experience and location. Nurse practitioners in obstetrics earn a higher salary, averaging $111,680 annually.
Resources for Obstetrics Nurses
Professional Organizations for Obstetrics Nurses
- Association of Women’s Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses (AWHONN): Offers continuing education, professional development, and resources for obstetrics nurses.
- National Perinatal Association (NPA): Works to improve maternal and fetal health through guidelines, education, and advocacy.
Continuing Education and Certification Resources
To stay current, obstetrics nurses can access a variety of professional development and certification opportunities, including those offered by AWHONN and the National Certification Corporation.
Networking Opportunities for OB/GYN Nurses
Joining professional organizations like AWHONN provides networking opportunities with other obstetrics nurses and healthcare professionals.

Dont wait until the last minute.
Provide your requirements and let our native nursing writers deliver your assignments ASAP.

