Comparing APA and MLA Formats
 In the realm of academic writing, adhering to specific formats is crucial.
In the realm of academic writing, adhering to specific formats is crucial.
Two commonly used formats are the APA and MLA essay formats.
To make an informed choice about the appropriate format for your essay, it’s important to understand the differences between APA and MLA formatting styles.
This understanding is particularly valuable for students tackling various assignments, including nursing papers, nursing assignments, and nursing exams.
APA and MLA: A Brief Overview
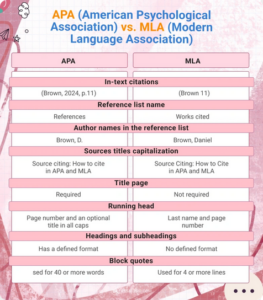
When examining the differences between APA and MLA formatting, you’ll notice subtle variations in their structure and application. MLA (Modern Language Association) is predominantly employed in arts and humanities, aiding in the citation of literary works, paintings, and historical texts. In contrast, APA (American Psychological Association) is tailored for technical endeavors prevalent in the social sciences, including psychology, sociology, and nursing research.

Struggling to meet your deadline?
Get your assignment on Comparing APA and MLA Formats done by certified MDs and PhDs in the USA. ORDER NOW!
The APA style is utilized for formatting journals, technical reports, and research papers. Both formats can be used to craft essays and papers, with the choice depending on the specific requirements of your discipline or instructor. Determining the right citation style, whether MLA or APA, can pose a challenge for students, particularly when navigating the complexities of academic writing.
The primary goal of both APA and MLA is to provide accurate citations, prevent plagiarism, and create high-quality papers adhering to the correct structure. This blog dissects the two styles separately to facilitate a clearer understanding, offering comprehensive guidance on selecting the best style for your assignment and the core standards of each.
Key Differences Between APA and MLA
To discern the differences between APA and MLA, let’s begin with their historical contexts and core philosophies. The MLA style is commonly applied in scientific research within the humanities field, emphasizing the author’s contributions and historical context. It offers comprehensive referencing and citation guidelines tailored to literary works.
Another distinction is that MLA emphasizes the author’s name and previous research, focusing on the text itself. In contrast, APA prioritizes the publication date of the referenced book or article, favoring recently published sources with pertinent information, which is particularly important in fields like nursing and psychology.
MLA Format Guidelines
The MLA format entails specific standards that must be followed for consistency and professionalism:
- Font and Spacing: Use Times New Roman font, size 12, with one-inch margins all around. The entire document should be double-spaced.
- In-Text Citations: Include the author’s name and page number in parentheses at the end of the cited sentence (e.g., Smith 23). There should be no comma between the name and the page number.
- Works Cited Page: At the end of your paper, include a “Works Cited” page that lists all sources referenced in alphabetical order. Each entry should follow specific MLA formatting rules, ensuring consistency.
- Title Formatting: Titles of essays and articles should be enclosed in quotation marks, with each significant word capitalized. The title of the paper should be centered and in plain text without italics or underlining.
Citing in MLA Format
To master MLA citing, referring to quality examples is essential. Acquiring these skills enhances your academic writing, allowing you to deliver high-quality assignments, dissertations, case studies, argumentative essays, and other academic works that require citations.
If you encounter difficulties in citing essays using MLA format, there’s no need to worry. This article encompasses vital elements of MLA citation, offering a comprehensive understanding of the style and examples for various types of sources.
Understanding MLA Style
The Modern Language Association (MLA) developed a writing style to enhance academic and scientific assignments, especially in the humanities. This association publishes guidelines that college students follow when working on projects. Depending on your research area, your instructor might request an MLA report, necessitating unique citations, a structured page outline, and adherence to the MLA guide.
Many students prefer the accessible nature of the MLA style. It’s easy to understand and apply, making it ideal for crafting drafts and submitting assignments. All MLA-cited papers must incorporate in-text citations in body paragraphs and a list of works cited at the paper’s end. This structured approach not only aids in clarity but also builds academic integrity by properly attributing sources.
APA Format Style
In educational settings, instructors often assign specific formatting for assignments. The APA format is a prevalent style for research papers, essays, and books, designed by the American Psychological Association for psychology and various sciences, including nursing.
APA format is commonly taught in schools and colleges to enhance academic writing skills. To grasp in-text APA citations, thorough perusal of examples is crucial. When employing APA citations, consider these key aspects of the style:
General Structure
An APA-style paper should include a title page, introduction, main body, references, footnotes, graphics, and appendices.
- Title Page: The title page, the paper’s first page, should feature the title at the center, your name, and your institution’s name. The running head should be at the page’s top, starting at the top left of each page. The running head should include fewer than 50 characters, including spaces.
- Introduction: The introduction, beginning on page two, features the term “Introduction” centered beneath the running head. It should contain a 100 to 200-word summary, outlining key research points and essay elements, such as the study’s hypothesis, methodologies, and conclusions. Avoid paragraph indentation in abstracts or introductions.
- Body Structure: The main body starts on page three and features a one-inch margin throughout. The left margin is flush, with paragraph beginnings indented five to seven spaces. Use Times New Roman font, maintain double spacing, and place page numbers in the top-right corner.
References and Citations
References pinpoint sources in your main body. Cite materials used for research and content development. Reference pages follow the main body, formatted with a hanging indent for each citation.
APA Style Features
To distinguish between APA and MLA in-text citations, explore the features or standards of each style. APA style incorporates:
- Double-spaced paragraphs.
- Times New Roman font, size 12, and one-inch margins.
- Page numbers at the upper right corner of each page.
- In-text citations with the author’s last name, publication year, and page number (e.g., Smith, 2020, p. 23).
- A specific formula for the author’s name in the reference list: Last name, First initial. (Year). Title of work. Publisher.
- Capitalization only for the first word of a title and subtitle, without quotation marks.
Similarities Between MLA and APA
Although distinct, MLA and APA share some similarities, making them both effective styles for academic writing:
- Both require a reference page at the end of the paper.
- They utilize double-spaced lines throughout the document.
- Times New Roman font, size 12, is standard for both styles.
- One-inch margins are necessary for consistency.
- Bibliographic lists of citations must be included in both formats.
Best Practices for Citing Sources
Understanding the best practices for citing sources in both MLA and APA formats is essential for producing high-quality papers, including custom nursing papers, nursing assignments, and nursing exams. Whether you’re writing nursing essays or conducting nursing research, knowing how to cite properly will enhance your credibility and academic integrity.
When selecting your citation style, consider the guidelines provided by your instructor or institution, as these can vary by field and assignment type. Here are some tips:
- Always keep track of your sources as you conduct research.
- Use citation management tools to help organize references.
- Familiarize yourself with the specific rules of the citation style you’re using, as both MLA and APA have their unique formats for different types of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.).
Conclusion
Appreciating the distinctions between APA and MLA formats is essential for selecting the appropriate style for your paper. This blog has delineated these differences and offered insights into citing both styles. By understanding the specific guidelines for each format, students can improve their academic writing and ensure they meet the requirements for high-quality work.
For further assistance, including resources for online nursing papers and additional writing tips, visit our website USAnursingpapers.com. Here, you’ll find tools and guidance tailored to help you excel in your academic endeavors, whether you’re tackling a complex nursing exam or crafting the best nursing papers.

Dont wait until the last minute.
Provide your requirements and let our native nursing writers deliver your assignments ASAP.

